AWS Transit Gateway
1. Creating the transit gateway in the AWS Console
1.1 Log in to AWS Console, navigate to Services/Networking & Content Delivery/VPC.
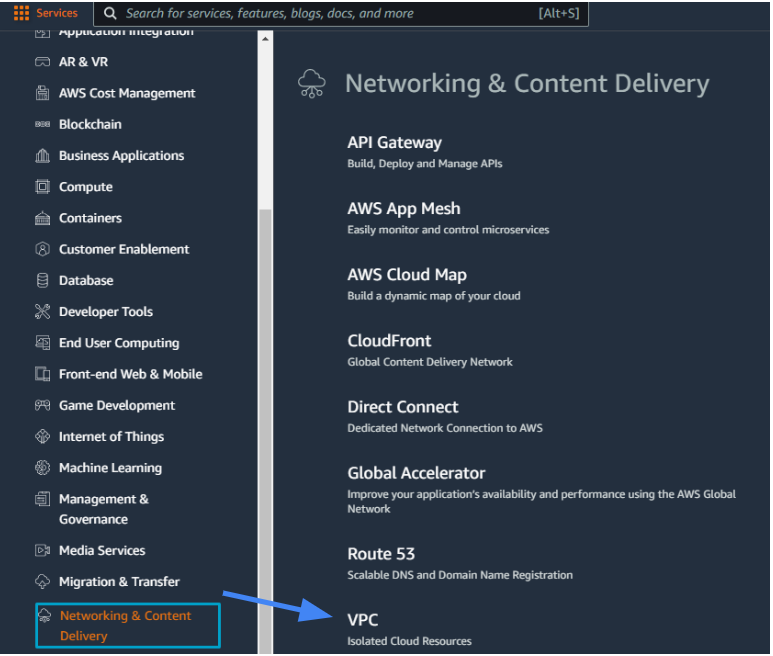
1.2 Under Virtual Private Network (VPN) create Transit Gateways.
1.3 Insert Name tag for transit gateway. You can leave remain values as a default.
-
Name tag - optional - Vipilink
-
Description -
-
Amazon side Autonomous System Number (ASN) -
-
DNS support - checked
-
VPN ECMP support - checked
-
Default route table association - checked
-
Default route table propogation - checked
-
Multicast support - unchecked
-
Auto accept shared attachments - unchecked
-
CIDR - optional -
**2. Creating the transit gateway attachments **
Notice
To enable communication between VPCs, VPNs, and Peered Transit Gateways located in different AWS regions, you must create attachments. These attachments allow connected resources to communicate with each other according to the routes defined in the Transit Gateway.
2.1 Go to Services/Networking & Content Delivery/VPC/Virtual Private Network (VPN) and create transit gateway attachments.

Details
-
Name tag - optional - Vipilink
-
Transit Gateway ID - choose the Transit gateway created in the Step 1
-
Attachment Type - VPC
VPC Attachment
-
DNS Support - Checked
-
VPC ID - choose appropriate VPC
Notice
Repeat Step 2.1 for each VPC that you want to gain access to.
3. Creating the transit gateway VPN attachment
3.1 Create another transit gateway attachment.
Details
-
Transit Gateway ID - choose newly created Transit Gateway
-
Attachment Type - VPN
VPN Attachment
-
Customer Gateway - New
-
IP Address - Vilipink Gateway Public IP
-
Routing Options - Static

4. Create the routing rules
4.1 Navigate to Virtual Private Cloud/Your VPCs and enter to routing table associated to VPC.
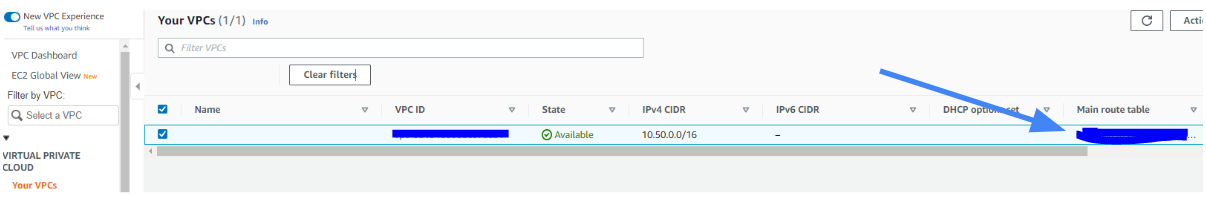
4.2. In Route tables menu again select the same route table and edit it. Add a route to Vipilink Local Subnet as a destination and VPN Gateway ID as a target.
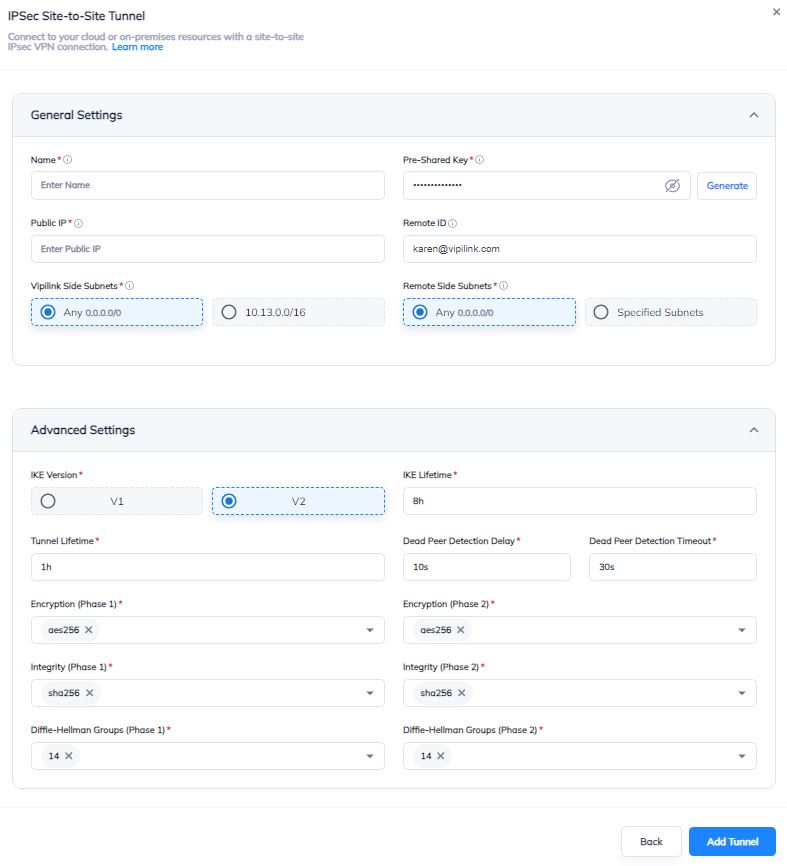
5. Creating tunnel in Vipilink Portal
5.1 Log in to Vipilink Portal and navigate to Networks, select the network and the gateway. Click on three-dotted menu (...) and Add Tunnel. Choose IPSec Site-2-Site Tunnel and create new tunnel.
General Settings Values
-
Name - AWS_Tunnel
-
Public IP - AWS VPC Public IP
-
Vipilink Side Subnets - 0.0.0.0/0
-
Pre-Shared Key - PSK generated at AWS
-
Remote ID - AWS VPC Public IP
-
Remote Side Subnets - 0.0.0.0
Advanced Settings Values
-
Ike Version - v2
-
Tunnel Lifetime - 1h
-
Encryption (Phase 1) - aes256
-
Integrity (Phase 1) - sha256
-
Diffie-Helman Groups (Phase 1) - 14
-
Ike Lifetime - 8h
-
Dead Peer Detection Delay - 10s
-
Dead Peer Detection Timeout - 30s
-
Encryption (Phase 2) - aes256
-
Integrity (Phase 2) - sha256
-
Diffie-Helman Groups (Phase 2) -14
5.2 Click on three-dotted menu (...) and add route to Routes Table. Subnet is AWS local network.
6.1 Verify connectivity between local and remote networks.
-
Use tools like ping or traceroute to check the connection
-
Ensure that resources on the remote network (e.g., shared folders, servers) are accessible from the local network.